Theories and Decidability
Theories and Decidability
Recall The 4 Questions we’re gonna answer.
Q1: What is a mathematical proof?
Q2: What makes a proof correct?
Q3: Is there a boundary of provability?
Q4: Can computers find proofs?
We’ve already answer Q1 Q2 & Q4.
Now we’re going to answer Q3.
Theories
First, give the definition.

我们还可以定义T 的逻辑闭包:

同样我们还可以知道以下3个命题是等价的
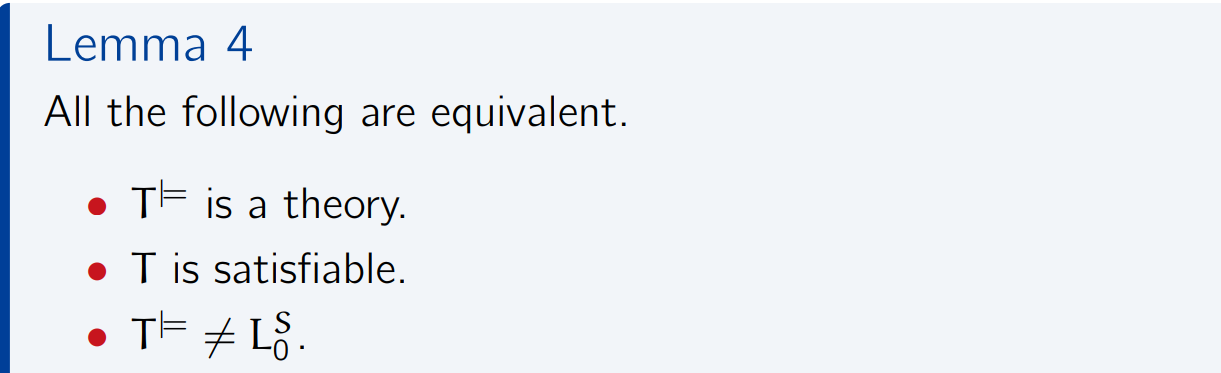
几个证明的关键点在:
- T T⊨ (取任意φ T;假设模型M 使得 M ⊨ T,则M ⊨ φ,故T ⊨ φ;所以有φ T⊨)
- 取模型M,如果M ⊨ T,可以取一个M无法满足的句子ψ,则ψ 不是T 的逻辑推论,则ψ 不属于T⊨
- T⊨是封闭的,因为对所有的ψ,如果(T⊨) ⊨ ψ,则T ⊨ ψ,则 ψ T⊨
- 空真:如果 T 不可满足,且T ⊨ φ,则φ可取任意L^S中公式
- 假设 T⊨ 不可满足,则 (T⊨)⊨ = L^S
Peano Arithmetic
φPA

Elementary arithmetic
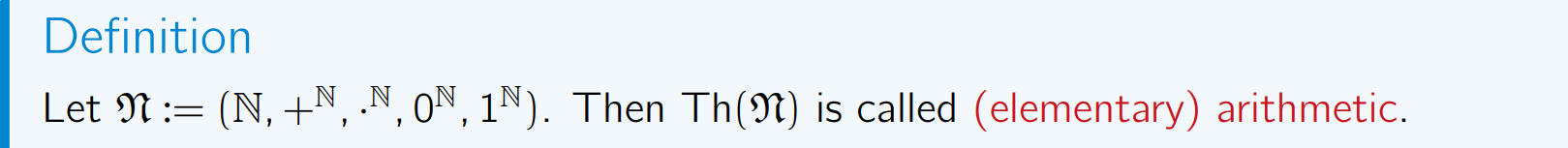
RMK:
It’s easy to see that φPA Th(N),we will show that φPA ⊊ Th(N)
R-axiomatizable 可公理化

Theorem 5
Every R-axiomatizable theory is R-enumerable.
Complete Theory
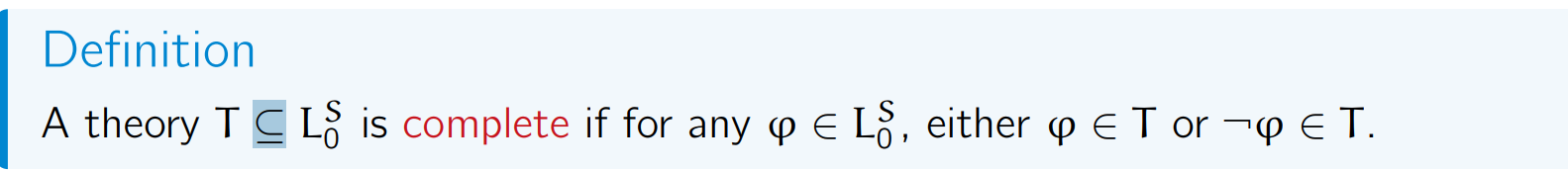
Theorem 6
(i) Every R-axiomatizable complete theory is R-decidable.
(ii) Every R-enumerable complete theory is R-decidable.
Theories and Decidability
https://janezair.site/2025/05/18/Mathematical-Logic12/