Graph Algorithms
ps: 上机课是05.18上的,算法是05.23学的🤣(评价是这周事还是太多了)perhaps和这节上机课量巨大也有关系吧😢
术语回顾
DAG 有向无环图
点度 = 入度 + 出度
SPT 最短路径树
最短路 单源/多源
Q:给出一个加权图和图上的一个节点s,找出s到图中每一节点的最短路径
Dijkstra 算法
Core:v=argmin_u∈SPT,(u,v)∈E,v∉SPT{d(s,u)+w(u,v)}
代码实现(使用pq进行优化):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #include <iostream> #include <queue> int end ;int weight;200005 ];void add_edge(int u,int v,int w){current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->weight = w;current ->next = G[u].head;current ;bool known[200005 ];int distance[200005 ];int dis;int u;bool operator <(const Pair &a)const{return dis > a.dis;int main(){int n,m;int start ;int u,v,w;start ;for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i ++){for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){false ;1e9 ;start ] = 0 ;0 ,start });while (!pq.empty()){if (known[top.u]){continue ;true ;current = G[top.u].head;while (current ){if (dis[current ->end ] > dis[top.u] + current ->weight){current ->end ] = dis[top.u] + current ->weight;current ->end ],current ->end });current = current ->next;
upd:改了一下Dijkstra的板子(某个🤡机考的时候Dijkstra板子写成了修改前的错误版本导致痛失70分😭😭😭)。
Bellman-Ford 算法
用于处理存在负边的图
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 #include <iostream> int end ;int weight;200005 ];void add_edge(int u,int v,int w){current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->weight = w;current ->next = G[u].head;current ;int distance[200005 ];int main(){int n,m;int start ;int u,v,w;start ;for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i ++){for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){false ;1e9 ;start ] = 0 ;bool flag = false ;for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){false ;for (int j = 1 ;j <= n;j ++){if (dis[current ] == 1e9 ){continue ;current = G[j].head;while (current ){if (dis[curent->end ] > dis[j] + current ->weight){current ->end ] = dis[j] + current ->weight;true ;current = current ->next;if (!flag){if (!flag){-1 ;//存在负权环return 0 ;
SPFA 算法 (已经死了)
虽然可以构造数据把BF的队列优化卡掉, 但还是学习一下这种优化吧,毕竟笔者刚做小作业时,第一遍BF 大T特T,第二遍SPFA 被卡了一个点,最后进行了SPFA + SLF优化才过。
首先是SPFA的队列优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 bool visit[25005 ];while (!q.empty()){false ;while (current){if (dis[current->end ] > dis[u] + current->dis [current->end ] = dis[u] + current->if (!visit[current->visit [current->true ;q .push(current->current = current->
我们继续观察,还可以发现,如果松驰后的顶点的dis越小,那么对后续产生的影响越大,可以往前放,于是我们首先想到是否可以用pq解决
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 dis[s] = 0 ;while (!q.empty()) {false ;while (current) {if (dis[current->end ] > dis[u] + current->dis [current->end ] = dis[u] + current->if (!visit[current->q .push(current->visit [current->true ;current = current->
确实优化了,但依然被助教卡了,主要还是因为pq凭空多了调整的logN级复杂度,那么还能怎么优化呢?
男明星:deque!双端队列使插入删除变为O(1)的复杂度,很好了🥰
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 dis[s] = 0 ;while (!q.empty()) {false ;while (current) {if (dis[current->end ] > dis[u] + current->dis [current->end ] = dis[u] + current->if (!visit[current->visit [current->true ;if (!q.empty() && dis[current->q .push_front(current->else {q .push_back(current->current = current->
这也就是传说中的 SPFA + SLF优化!妙啊!(使我不用写Dijkstra + 连通分量的正解了XD)
Floyd 算法
用于多元最短路问题 (求任意两个结点之间最短路)
类似BF的dp思路,维护一个三维数组 d[k,u,v],表示只允许经过 1-k 的顶点,结点u到结点v 的最短路长度
状态转移方程为:
从 u 到 v 经过 k 或者不经过 k
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 for(int k = 1;k <= n;k ++){
例题
贴个题: 裂点
省流:
1 n 个点 m 条有向边,边有正边权,可以免费走 k 条边,边权视为 0 ,求 s 到 t 的最短路
想法:
则(u,f) -> (v,f) 边权w
用Dijkstra即可
连通分量
Concept Recall
连通性是二元等价关系(自反性、对称性、传递性)
有向图中,弱连通:转向无向图后连通;
强连通分量(SCC)是等价类,将点集划分成若干个内部强连通的部分
强连通分量算法
Kosaraju 算法
从任意结点开始对有向图进行深度优先搜索,得到一个深度优先森林
将节点遍历:按照生成树的次序 + 对每一棵树上的节点进行后序遍历
将图 G 逆向得到Gr
从编号最大的节点开始深度优先搜索,得到的森林就是原图的强联通分量。
代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std;int end ;int weight;25005 ];//正向图25005 ];//反图void add_edge1(int u,int v,int c) {current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->weight = c;current ->next = G1[u].head;current ;void add_edge2(int u,int v,int c) {current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->weight = c;current ->next = G2[u].head;current ;int n,m;bool visit[25005 ];bool colored[25005 ];int > s;int SCCcnt;void dfs1(int u){true ;current = G1[u].head;while (current ){if (!visit[current ->end ]){current ->end );current = current ->next;void dfs2(int u){current = G2[u].head;while (current ){if (!colored[current ->end ]){current ->end );current = current ->next;int main(){for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i ++){int u,v,w;for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){if (!visit[i]){for (int i = n;i >= 1 ;i if (!colored[s[i]]){ //还未被分配到任何SCC中
Tarjan 算法
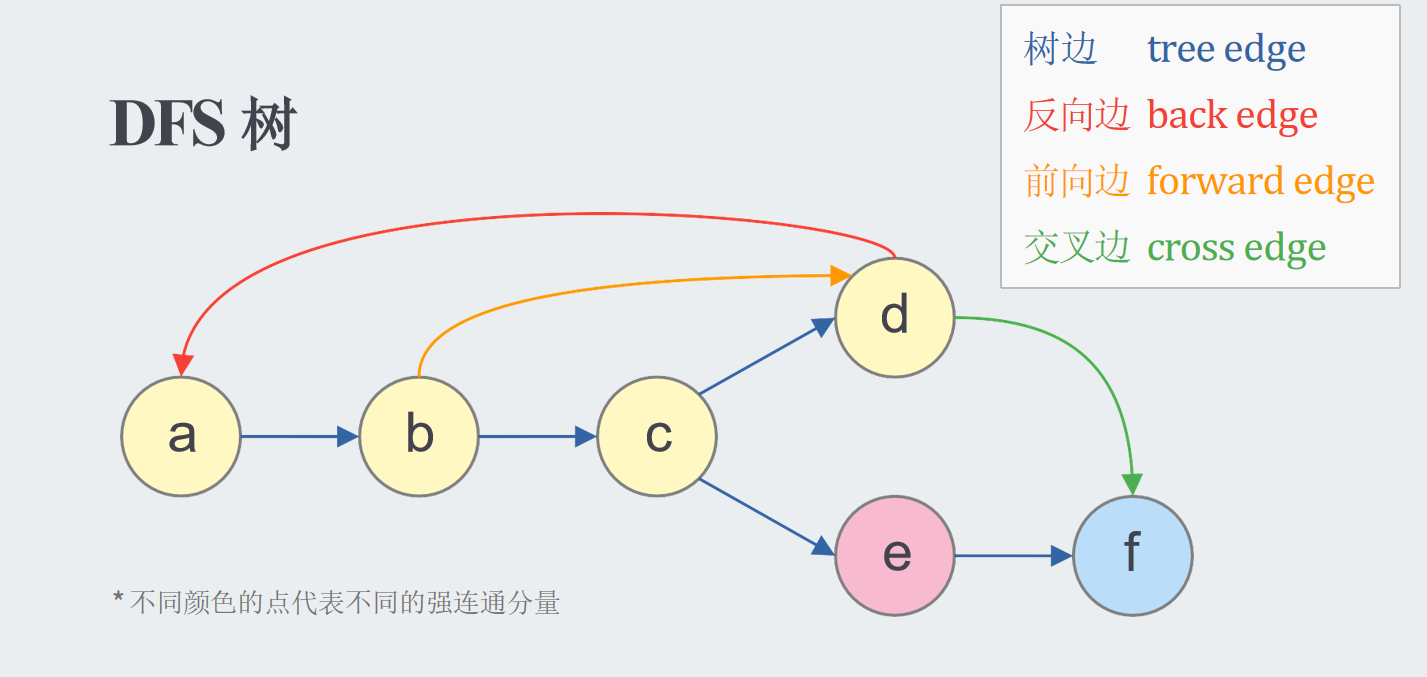
在DFS过程中,按照生成的顺序会生成一颗结构良好的DFS树。DFS得到的序列(DFS序并不能保证相邻节点一定有边相连),但是DFS树的节点一定都是图中的节点,换句话说,DFS树在本质上就是一个在中序遍历上完全等价的树。
但是很显然,一颗DFS树上的顶点不代表联通。我们需要考虑不在DFS树上的边,例如这里的:
Lemma: SCC 中 dfn 最小的结点是该 SCC 中所有节点在 DFS 树上的祖先(也就是所谓最远能到达的祖先)
Tarjan 算法实现
用一个栈表示没有全部访问的 SCC
一个点的所有边访问结束之后,若 dfn[v ] = low[v ] ,则 v 及其子树的一部分构成一个 SCCLemma: dfn[v] = low[v] 的点是其所在 SCC 中 dfn 最小的点
Tarjan算法的原理是笔者学过所有算法中最恶心最绕的😅,但它的实现还是挺容易的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 int dfn[200005 ];int low[200005 ];int dfnCnt;int Stack[200005 ];//一个栈,用于跟踪当前正在进行 DFS 遍历的路径上的节点。节点在被发现时入栈,在找到一个强连通分量时出栈bool inStack[200005 ];//是否在栈中int top;//栈顶指针int scc[200005 ];//结点i所在强连通分量编号int sccCnt;//强连通分量个数计数器int sz[200005 ];//强连通大小void Tarjan(int u){true ;current = G[u].head;while (current ){if (!dfn[current ->end ]){current ->end );current ->end ]);else if (inStack[current ->end ]){current ->end ]);current = current ->next;if (dfn[u] == low[u]){do {false ;while (Stack[top int main(){for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++){if (!dfn[i]){
一道很棒的Tarjan例题(算是自己做出来的一道蓝题吧)
老规矩,贴题,ATM
相当综合的一题,把笔者今天学的近乎所有图算法都用了一遍🤣🤣🤣
贴个AC代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;int n,m;int s,p;int sccCnt;int SCC[500005 ];int Stack[500005 ];int top;int dfn[500005 ];int dfnCnt;int low[500005 ];bool inStack[500005 ];int Money [500005 ];//每个路口的钱int sccMoney[500005 ];//每个强连通分量中抢到钱的总数bool sccPub[500005 ];//每个强连通分量中是否有pubbool pub[500005 ];//酒吧位置int end ;500005 ];void add_edge(int u,int v) {current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->next = G[u].head;current ;void tarjan(int u) {true ;current = G[u].head;while (current ) {if (!dfn[current ->end ]) {current ->end );current ->end ]);else if (inStack[current ->end ]) {current ->end ]);current = current ->next;if (dfn[u] == low[u]) {do {false ;Money [Stack[top]];if (pub[Stack[top]]) {true ;while (Stack[top 500005 ];void add_edgeNEW(int u,int v) {current = new edge;current ->end = v;current ->next = newG[u].head;current ;int dis[500005 ];bool visit[500005 ];int main() {for (int i = 1 ;i <= m;i ++) {int u,v;for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++) {Money [i];for (int i = 1 ;i <= p;i ++) {int pos;true ;for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++) {if (!dfn[i]) {for (int i = 1 ;i <= n;i ++) {current = G[i].head;int nCurrent = SCC[i];while (current ) {int nEnd = SCC[current ->end ];if (nEnd != nCurrent){current = current ->next;int start = SCC[s];//起始强连通分量int > q;start );start ] = sccMoney[start ];while (!q.empty()) {int top = q.front();false ;current = newG[top].head;while (current ) {if (dis[current ->end ] < dis[top] + sccMoney[current ->end ]) {current ->end ] = dis[top] + sccMoney[current ->end ];if (!visit[current ->end ]) {current ->end ] = true ;current ->end );current = current ->next;int MaxMoney = 0 ;for (int i = 1 ;i <= sccCnt;i ++) {if (sccPub[i]) {if (dis[i] > MaxMoney) {return 0 ;
Reference
Thanks so much:
Final Words
做完了最后一次小作业的最后一题,再加上周四已经通过的火车票管理系统,数据结构CS1951 的所有课程内容都基本完成了(还有个机考😭)。感觉一学期下来代码能力得到了不小的提升(虽然这学期好像也没写什么代码🤣)。有一点怅然若失,每天写学算法、写小作业、debug大作业的日子就这样过去了,但想到未来还会学更多有趣的东西,又觉得很兴奋。或许一年前的我,还在为差一点点就能去清北,而质疑自己的选择,但我想我不会后悔我做的每一个决定。也有人问我家那么富为什么要来学cs😅,但我对钱真的不感兴趣呢。一直认为自己物欲很低(室友锐评:清心寡欲),没什么特别想要的,花钱很少,觉得钱没那么重要,也不想靠父母活一辈子(如果我这么选,我甚至不用上大学😅)。